Unlike fiat currencies, such as the Euro or the U.S. Dollar, the value of Bitcoin (BTC) is not defined by a single entity like a central bank. Instead the price is defined by supply and demand, or in simpler terms, by the price people are willing to pay for it.
Lets first understand what influences the Price
The price of a Bitcoin is determined by supply and demand. When demand for Bitcoins increases, the price increases, and when demand falls, the price falls. The supply is fixed to 21,000,000 BTC. Therefore, there is only a limited number of Bitcoins in circulation and new Bitcoins are created at a predictable and decreasing rate, which means that demand must follow this level of inflation to keep the price stable. Because Bitcoin is still a relatively small market compared to what it could be, it doesn't take significant amounts of money to move the market price up or down, and thus the price of a Bitcoin is still very volatile.
Bitcoin’s supply and demand can be influenced by the following factors:
- The current supply of Bitcoin.
- The cost of producing a Bitcoin through the mining process.
- The rewards issued to Bitcoin miners for verifying transactions to the blockchain.
- The number of competing cryptocurrencies.
- The exchanges it trades on.
- Regulations governing its sale.
- Its internal governance.
- News, economy, public opinion.
As alluded, Bitcoin protocol allows new Bitcoins to be created at a fixed rate. New Bitcoins are introduced into the market when miners process blocks of transactions and the rate at which new coins are introduced is designed to slow over time. Case in point: growth has slowed from 6.9% (2016), to 4.4% (2017) to 4.0% (2018). This can create scenarios in which the demand for Bitcoins increases at a faster rate than the supply increases, which can drive up the price. The slowing of Bitcoin circulation growth is due to the halving of block rewards offered to Bitcoin miners and can be thought of as artificial inflation for the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
So, how to determine Bitcoin price at any given point of time?
Bitcoin’s price isn’t set by anyone in particular. It’s set by the market. This makes pricing the currency more complex because prices will vary by exchange. Bitcoin is never traded in one place. Instead, it is traded on multiple exchanges, all of which set their own average prices, based on the trades being made by the exchanges at a given time. You aren't able to trade bitcoin via these index sites - all they’re doing is aggregating price information.
If you want to buy and sell bitcoin, you have to choose a particular exchange, which will have its average price. The price of bitcoin fluctuates at any given moment, depending on which exchange the information comes from. It’s also worth noting that different exchanges have different price algorithms. This will also be a factor in price listings since some may process faster than others.
The price at any moment is a natural result of the trading that happens on cryptocurrency exchanges in a process called price discovery. For example, consider Coinbase, a popular U.S. hub for people who want to buy or sell Bitcoin. If you purchase there, the entity selling you the cryptocurrency is actually Coinbase itself. Coinbase has a sister site, called GDAX, which stands for Global Digital Asset Exchange. GDAX is now re-named Coinbase Pro. It is a marketplace for professional traders and institutions, and that's where the price discovery happens. The price of the last trade on Coinbase Pro is the value of Bitcoin there at the moment, and that's also the basis for the price you see on Coinbase.
Coinbase Pro operates a continuous first-come, first-serve order book. Orders are executed in price-time priority as received by the matching engine. For example, User A places a Buy order for 1 BTC at $10,000 USD. User B then wishes to sell 1 BTC at $8,000 USD. Because User A's order was first to the trading engine, they will have price priority and the trade will occur at $10,000 USD.
But, why is Bitcoin price volatile?
Bitcoin has the highest trading volume among cryptocurrencies and you can buy and sell in fractions, but it’s still a small market compared to other global markets. This means that prices make bigger moves up or down with less money involved. If Bitcoin were to have the same trading volume as, for example, gold, then its behavior would be very similar in terms of volatility.
As there are only a limited number of Bitcoins in circulation, and the creation of new Bitcoins follows strict rules with a consistently decreasing output (because of shrinking rewards for miners), demand would have to follow the deflationary behavior of Bitcoin to even theoretically keep prices stable. Volatility is measured by sampling how far away Bitcoin’s price goes from the price at a fixed point in time. In our case, Bitcoin’s opening price on a specific day.
Conclusion
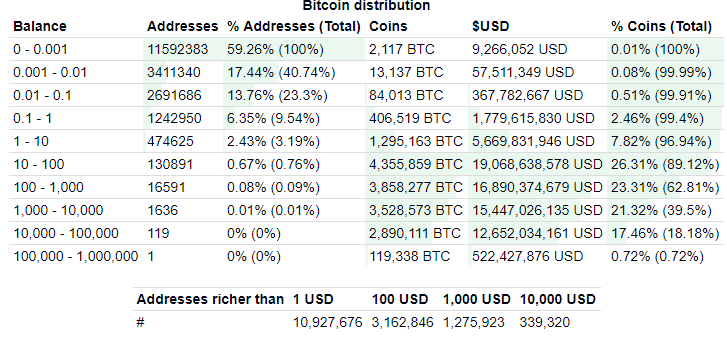
Supply and demand, in economics, is the relationship between the quantity of a commodity that producers wish to sell at various prices and the quantity that consumers wish to buy. It is the main model of price determination used in economic theory. However, some feel that Bitcoin price can be subjected to market manipulation. A forensic study on bitcoin's 2017 boom, by professors at University of Texas and the Ohio State University, found that nearly the entire rise of the digital currency at the time is attributable to "one large player," although the market manipulator remains unidentified. But as Bitcoin adoption grows and more and more people own bitcoin even in fractions, the number of large players will decrease. Below is the current distribution of Bitcoins.
So, what is the future Price of Bitcoin? It is hard to tell but if demand and adoption continues to grows, the price should trend upwards given the fix supply of Bitcoins.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes, and is not intended to influence people's investment options.